Nearly 20 million new cases of sexually transmitted diseases affect people in the United States each year, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. With these highly preventable diseases often come symptoms that affect your entire body – including your mouth. Not all people who are infected will go on to have symptoms. If a person with a sexually transmitted infection (STI) develops symptoms, they are then considered to have a sexually transmitted disease (STD).
While not all STDs are curable, they are treatable. Your dentist is an important part of your healthcare team. Use this visual guide to learn how these infections can impact your mouth.
Please note: This content is for informational purposes only. Only a dentist, physician or other qualified health care professional can make a diagnosis. To learn more about preventing sexually transmitted diseases, visit CDC.gov.
HPV: Oral Cancer

The human papilloma virus (HPV) is the most common sexually transmitted disease in the United States, with 14 million new cases each year. According to the CDC, there are more than 40 types of HPV, but most are cleared from the body by the immune system without causing any health problems.
HPV can affect the mouth and throat. Some high-risk strains are associated with head and neck cancers, including oral cancer. Approximately 9,000 cases of HPV-related head and neck cancers are diagnosed each year. The CDC states these cancers are four times more common in men than in women.
These cancers typically develop in the throat at the base of the tongue and in the folds of the tonsils, making them difficult to detect. Although people with HPV-positive cancers have a lower risk of dying or having recurrence than those with HPV-negative cancers, early diagnosis is the associated with the best outcomes. Regular dental check-ups that include an examination of the entire head and neck can be vital in detecting cancer early.
HPV: Mouth Warts

Low-risk strains of HPV may cause warts or lesions in your mouth or throat. The image above is an example of a deep lesion. Aside from their appearance, they often have no (or very few) symptoms, are painless and non-cancerous. They can reappear from time to time, and your dentist or physician may recommend having them surgically removed.
Herpes
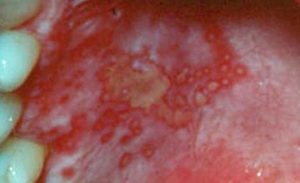
There are two strains of the virus that causes herpes. Currently, there is no cure for either strain. Herpes simplex virus type 1 is most commonly associated with cold sores and other mouth lesions. Herpes simplex virus type 2 is most commonly associated with genital lesions. However, both strains are extremely contagious and can be passed between the genitals and the mouth through saliva and contact with open sores during and right before an outbreak.
During an outbreak, you may see blisters in your mouth. Their appearance varies widely. They could be clear, pink, red, yellow or gray. When they pop, you may feel pain when you try to swallow or eat. They generally heal within 7-10 days, and your dentist can prescribe medicine to reduce the pain. Symptoms of herpes can so include fever and fatigue. Be sure to talk to your physician about the best way for you to manage the disease.
Syphilis
Syphilis has been on the rise since 2005 and reached its highest reported rate in 2015. Nearly 24,000 cases were reported in 2015, a 19% increase over the 19,999 cases reported in 2014.
During the first stage of infection, syphilis may appear as sores, known as chancres, on your lips, the tip of your tongue, your gums or at the back of your mouth near your tonsils. They start as small red patches and grow into larger, open sores that can be red, yellow or gray in color. These are very contagious and often painful. If untreated, the sores may go away, but you still have syphilis and can infect others.
Syphilis is a bacterial infection that is actually very treatable in its early stages. Your dentist can do a biopsy to confirm a diagnosis. If positive, you would be referred to your primary care physician for more testing and treatment. But it is important to be aware that untreated syphilis can cause long-term damage to your heart and brain.
Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection that affects mucous membranes, including those in your mouth and throat. As with syphilis, the number of cases of gonorrhea cases is also at an all-time high. In 2015, nearly 400,000 cases were reported. That’s a 13% increase over the 350,062 cases reported in 2014.
Gonorrhea can be difficult to detect because its symptoms are often very mild and can go unnoticed. The most common symptoms in your mouth are soreness or burning in your throat. Additional symptoms may include swollen glands and occasionally white spots in your mouth.
Untreated gonorrhea can cause seriously impact your health. A throat culture swab test can diagnose gonorrhea if you have symptoms in your mouth. Discuss any concerns about your mouth or throat with your dentist, and see your physician for further testing and treatment.